Egypt Geography & the Gift of the Nile

Essential Themes
Geography: Why do people move and live where they do?
Welcome to Ancient Egypt!
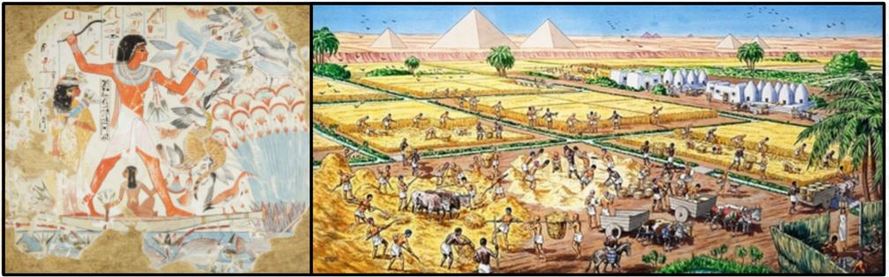
The ancient Egyptians were fascinating people and, thanks to the movies, they are too often misunderstood. It is true, of course, that the ancient Egyptians left behind towering monuments and elaborate tombs for their dead leaders. While the pyramids do stand as memorials to the Pharaohs, they are also reminders of their achievements in life. Indeed, the ancient Egyptians were not in love with death, but with life! They enjoyed their life to the fullest. They worked hard, but they saved time to enjoy family, friends, music, parties, swimming, fishing, hunting, sailing, and especially their children, all of which were very important to the ancient Egyptians.
Geography: Why do people move and live where they do?
Welcome to Ancient Egypt!
The ancient Egyptians were fascinating people and, thanks to the movies, they are too often misunderstood. It is true, of course, that the ancient Egyptians left behind towering monuments and elaborate tombs for their dead leaders. While the pyramids do stand as memorials to the Pharaohs, they are also reminders of their achievements in life. Indeed, the ancient Egyptians were not in love with death, but with life! They enjoyed their life to the fullest. They worked hard, but they saved time to enjoy family, friends, music, parties, swimming, fishing, hunting, sailing, and especially their children, all of which were very important to the ancient Egyptians.
Animals were very important to the ancient Egyptians. Unlike other ancient cultures, whose gods looked somewhat like people, most ancient Egyptian gods had animal heads. Cats, especially, were held in high esteem. The ancient Egyptians believed that cats had magical powers. They believed cats protected their homes and children from danger, and helped their crops to grow. The ancient Egyptians carefully protected their cats. Any person who killed a cat paid for that crime with their life!
The ancient Egyptians believed in an afterlife. They believed that people enjoyed many of the same activities in their afterlife as they did in their current life. They prepared for their afterlife by filling their tombs with small and large statues of friends and family, with household items, and with other items they might need to keep them company and to help them have a good time.
While it’s easy to connect the ancient Egyptians to the pyramids in our minds, sometimes it’s harder to imagine just how influential Egyptian culture was on other ancient civilizations that existed at the same time. Ancient Greece and Rome, especially, owe a debt to Egyptian art, architecture, and politics. More, Egypt managed to stay alive as a civilization for over 4000 years. How were they able to maintain that continuity? Part of the answer lies in their geography.
The ancient Egyptians believed in an afterlife. They believed that people enjoyed many of the same activities in their afterlife as they did in their current life. They prepared for their afterlife by filling their tombs with small and large statues of friends and family, with household items, and with other items they might need to keep them company and to help them have a good time.
While it’s easy to connect the ancient Egyptians to the pyramids in our minds, sometimes it’s harder to imagine just how influential Egyptian culture was on other ancient civilizations that existed at the same time. Ancient Greece and Rome, especially, owe a debt to Egyptian art, architecture, and politics. More, Egypt managed to stay alive as a civilization for over 4000 years. How were they able to maintain that continuity? Part of the answer lies in their geography.
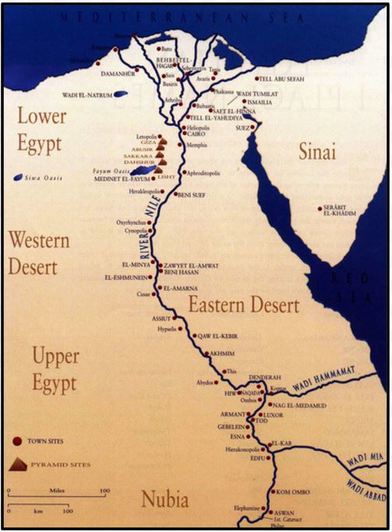
How did natural barriers influence the development of ancient Egypt?
Geography of Egypt: Egypt’s unique geography isolated Egypt from much of the rest of the early ancient world. In the formative years of Egyptian civilization, that isolation was an advantage. It allowed the civilization to grow and prosper. Later, Egypt's robust agriculture - made possible by one of Egypt's key geographical features, the waters of the Nile River - was the envy of other civilizations and helped connect the Egyptians to peoples around the Mediterranean.
The Gifts of the Nile: Imagine a deep blue river and a wide azure sky. Now, picture lush green plants and brown bluffs along the shoreline. When you do that, you’ve begun to imagine ancient Egypt. Because of the black sediment left behind after the frequent floods, the ancient Egyptians called the river Ar or Aur, which means "black." Today we know this river as the Nile. The name comes from the Greek Neilos, which means "river valley."
Geography of Egypt: Egypt’s unique geography isolated Egypt from much of the rest of the early ancient world. In the formative years of Egyptian civilization, that isolation was an advantage. It allowed the civilization to grow and prosper. Later, Egypt's robust agriculture - made possible by one of Egypt's key geographical features, the waters of the Nile River - was the envy of other civilizations and helped connect the Egyptians to peoples around the Mediterranean.
The Gifts of the Nile: Imagine a deep blue river and a wide azure sky. Now, picture lush green plants and brown bluffs along the shoreline. When you do that, you’ve begun to imagine ancient Egypt. Because of the black sediment left behind after the frequent floods, the ancient Egyptians called the river Ar or Aur, which means "black." Today we know this river as the Nile. The name comes from the Greek Neilos, which means "river valley."

The Nile River is the longest river in the world. It is over 4000 miles long and flows through nine African nations. It starts in the mountains in Central Africa and flows north, downhill, to the Mediterranean Sea. That’s why Lower Egypt is located to the north and Upper Egypt is located to the south, on higher ground. The Nile is shaped like the lotus flower so often seen in ancient Egyptian art and hieroglyphs. The stalk is a long swaying curve and the flower is the river's fan shaped delta at the end, where the Nile empties into the Mediterranean Sea.
The Nile is surrounded on four sides by natural barriers. A natural barrier is a physical feature that protects or hinders travel through or over land. Mountains, swamps, deserts, icefields, and bodies of waters such as rivers, large lakes, and seas are examples of natural barriers. To Egypt’s north lays the Mediterranean Sea. To the East of the Nile is the Eastern Desert and the Red Sea. To the west of the Nile is the Western Desert. And, to the south are mountains that hold the headwaters of the Nile. The natural barriers that surrounded the Nile River protected the people who settled and lived along the Nile’s fertile riverbanks.
The Nile is surrounded on four sides by natural barriers. A natural barrier is a physical feature that protects or hinders travel through or over land. Mountains, swamps, deserts, icefields, and bodies of waters such as rivers, large lakes, and seas are examples of natural barriers. To Egypt’s north lays the Mediterranean Sea. To the East of the Nile is the Eastern Desert and the Red Sea. To the west of the Nile is the Western Desert. And, to the south are mountains that hold the headwaters of the Nile. The natural barriers that surrounded the Nile River protected the people who settled and lived along the Nile’s fertile riverbanks.
How did the annual flood of the Nile help the ancient Egyptians?
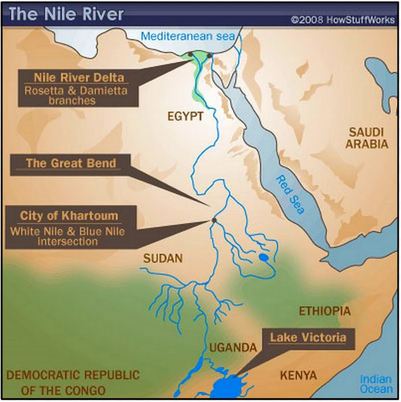
The Nile itself is a most unusual river. In central Africa, three lakes each provide a stream of water flowing towards the Mediterranean Sea to the north. Two of these streams combine quite early. One stream is called the White Nile. The other stream is called the Blue Nile. It joins the White Nile about half way along. For the last 2,000 miles, the river is simply called the Nile. At the Nile’s northern end, near the Mediterranean, the Nile breaks up into many smaller rivers and streams and marshland, forming a broad V. That V forms the famous and fertile delta of Lower Egypt.
Civilization started along the Nile about 5,000 years ago. Because it rarely rains, without the Nile all of Egypt would be a desert. Because of the Nile and the many gifts provided by the Nile, however, compared to other ancient civilizations, the ancient Egyptians enjoyed a high standard of living and a relatively peaceful life.
Civilization started along the Nile about 5,000 years ago. Because it rarely rains, without the Nile all of Egypt would be a desert. Because of the Nile and the many gifts provided by the Nile, however, compared to other ancient civilizations, the ancient Egyptians enjoyed a high standard of living and a relatively peaceful life.
Gifts of the Nile included water, transportation, trade, papyrus, fish and other animals, and rich black soil. It all started each year with the annual slow flooding of the Nile. The annual flood is often called the inundation. A flood doesn’t sound like much of a gift, but it was.
Unlike flooding in ancient Mesopotamia or China, flooding of the Nile was gentle and regular, following a dependably routine cycle:
Unlike flooding in ancient Mesopotamia or China, flooding of the Nile was gentle and regular, following a dependably routine cycle:
|
|
|
Besides the rich, black soil, what are some other "gifts of the Nile?"
AGRICULTURE: The ancient Egyptians built irrigation ditches that led from the river to their crops. As the floodwaters rose slowly and predictably each year, the irrigation ditches filled with water. As the water receded, the farmers blocked the irrigation ditches to keep the water inside, water they used to help them grow crops in the rich black soil. |

They invented the shaduf (pronounced sha-doof) to help them lift water from the canals to the crops. A shaduf is a bucket on a rope that hangs from a frame on a pivot. They dipped the bucket in the water, and spun the shaduf around so they could empty the bucket on the crops. With the shaduf, the ancient Egyptians no longer had to hand carry water. Instead, they used the shaduf to lift the water for them. Invention of the shaduf saved a lot of labor then and is still used along the banks of the Nile to this day.
The Egyptians grew figs, onions, pomegranates, apples, beans, garlic, chick peas, radishes, spinach, turnips, lettuce, carrots, cucumbers, melons, pumpkins, grapes, barley (used to make bread and beer) and flax (used to make clothes). The ancient Egyptians also built dams, to keep a supply of water handy in case of drought.
The Egyptians grew figs, onions, pomegranates, apples, beans, garlic, chick peas, radishes, spinach, turnips, lettuce, carrots, cucumbers, melons, pumpkins, grapes, barley (used to make bread and beer) and flax (used to make clothes). The ancient Egyptians also built dams, to keep a supply of water handy in case of drought.
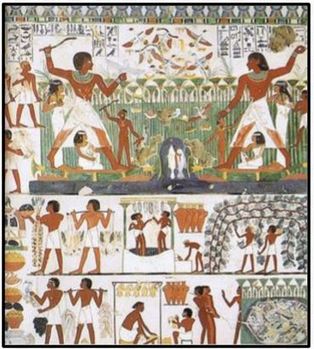
PASTURELAND: The Nile provided pastureland. Herdsmen and shepherds pastured their animals in the marshes along the Nile. Beef, oxen, sheep, and goats provided meat, milk, hides and dung for cooking fuel. Milk was highly prized, as was butter.
FISH & GAME: The Nile was rich with food. Eggs were plentiful. There were ducks and wild geese and quails and water birds, as well as bigger animals like crocodile and hippopotamus. Fish was eaten by the lower classes.
DRINKING WATER: The Nile was a river, not a salty sea. That meant the ancient Egyptians could drink the water, wash their clothes, and bathe (which they did daily).
FISH & GAME: The Nile was rich with food. Eggs were plentiful. There were ducks and wild geese and quails and water birds, as well as bigger animals like crocodile and hippopotamus. Fish was eaten by the lower classes.
DRINKING WATER: The Nile was a river, not a salty sea. That meant the ancient Egyptians could drink the water, wash their clothes, and bathe (which they did daily).
PAPYRUS: A plant called papyrus grew wild along the riverbanks of the Nile. The ancient Egyptians used papyrus to make paper, to build boats, to make sandals for their feet, and to make baskets to store their belongings and to carry their food. Because wood was scarce, boats were also made out of papyrus.
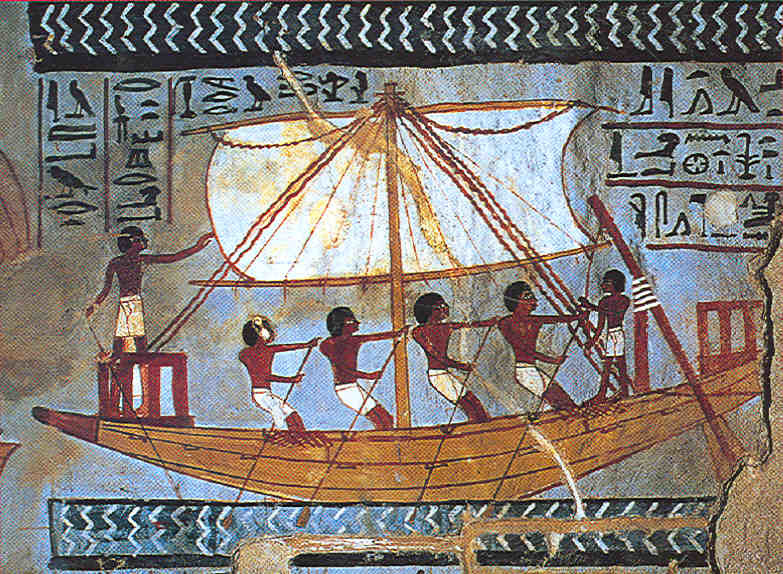
TRANSPORTATION & TRADE: The Nile provided an easy, cool transportation route. It was a major trade route. The ancient Egyptians had cargo boats, passenger boats, funeral boats, and naval vessels. The prevailing wind along the Nile blows south, and the current flows north. The ancient Egyptians hoisted sails on their boats to sail upstream (south), and used the Nile’s natural current to help them boat downstream (north). This made travel up and down the Nile very easy!
BUILDING MATERIAL: The Nile provided not only rich deposits of black soil, but also created rich deposits of clay, granite, sandstone, and limestone used for building. The ancient Egyptians built their homes out of stone and clay, not wood. Wood was scarce.
THE ARTS: You can imagine what a worry it was – would the Nile flood again this year? The Nile was incredibly important to the ancient Egyptians. They sang songs and created myths and stories to honor and to explain the wonderful Nile. They were very grateful for all her many gifts. Here is an example of a poem written to praise the Nile:
TRANSPORTATION & TRADE: The Nile provided an easy, cool transportation route. It was a major trade route. The ancient Egyptians had cargo boats, passenger boats, funeral boats, and naval vessels. The prevailing wind along the Nile blows south, and the current flows north. The ancient Egyptians hoisted sails on their boats to sail upstream (south), and used the Nile’s natural current to help them boat downstream (north). This made travel up and down the Nile very easy!
BUILDING MATERIAL: The Nile provided not only rich deposits of black soil, but also created rich deposits of clay, granite, sandstone, and limestone used for building. The ancient Egyptians built their homes out of stone and clay, not wood. Wood was scarce.
THE ARTS: You can imagine what a worry it was – would the Nile flood again this year? The Nile was incredibly important to the ancient Egyptians. They sang songs and created myths and stories to honor and to explain the wonderful Nile. They were very grateful for all her many gifts. Here is an example of a poem written to praise the Nile:
When the Nile is sluggish, the nostrils are stopped up and the people are brought low,
The offerings of the gods are reduced and millions die.
When the Nile rises, the Earth is joyous and everyone is glad,
Every jaw laughs and every tooth is uncovered.
The offerings of the gods are reduced and millions die.
When the Nile rises, the Earth is joyous and everyone is glad,
Every jaw laughs and every tooth is uncovered.
BRAINBOX: In one word, what is the "Gift of the Nile?"