Rome Barbarians Inside the Gates
Essential Themes
Conflict & Cooperation: How has warfare shaped human history?
The decline of the Western Roman Empire took place over many years. Its final collapse was the result of worsening internal problems, the separation of the Western Empire from the wealthier Eastern part, and outside invasions.
Conflict & Cooperation: How has warfare shaped human history?
The decline of the Western Roman Empire took place over many years. Its final collapse was the result of worsening internal problems, the separation of the Western Empire from the wealthier Eastern part, and outside invasions.

Brain Box: How would you describe the period of time that followed the Pax Romana?
A Troubled Empire
The peace of the Pax Romana begun during the rule of Caesar Augustus was followed by a century of confusion and violence. The Roman government grew weak while its army grew strong and independent. The legions of the army fought each other to put new emperors on the throne. In a period of just 50 years, Rome had 22 emperors.
This period of civil war caused great suffering. Food shortages led to higher prices, and because citizens were spending more of their money on basic necessities they often failed to pay taxes. The government tried to fix the economy by simply making more new coins. Flooding the marketplace with new coins, however, meant that the money had less value. As a result, prices continued to rise and it cost ever more money to buy goods. This is called inflation. Inflation happens when prices go up and money is worth less.
Why did Germanic tribes invade Roman territories?
A Troubled Empire
The peace of the Pax Romana begun during the rule of Caesar Augustus was followed by a century of confusion and violence. The Roman government grew weak while its army grew strong and independent. The legions of the army fought each other to put new emperors on the throne. In a period of just 50 years, Rome had 22 emperors.
This period of civil war caused great suffering. Food shortages led to higher prices, and because citizens were spending more of their money on basic necessities they often failed to pay taxes. The government tried to fix the economy by simply making more new coins. Flooding the marketplace with new coins, however, meant that the money had less value. As a result, prices continued to rise and it cost ever more money to buy goods. This is called inflation. Inflation happens when prices go up and money is worth less.
Why did Germanic tribes invade Roman territories?
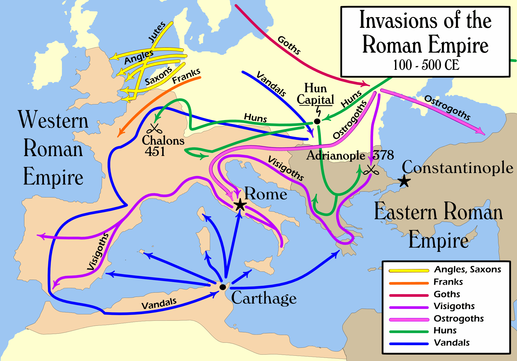
As Rome struggled, Germanic tribes began to attack the empire. Since the days of Julius Caesar, Germanic peoples had gathered on the northern borders of the Empire. Some groups settled into a peaceful farming life and adopted Roman ways, such as speaking Latin and becoming Christians. Other groups remained nomads. From 376 to 476 CE, huge numbers of Germans poured into Roman territory. As a result, Germanic tribes that included Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Franks, Angles, Saxons, Burgundians, Alemanni, and Vandals all competed for land, recognition, and Roman favor. Gradually, they overwhelmed the structures of Roman society. Finally, they drove the last Roman emperor from the throne.
The Huns Move West
The main reason for the Germanic invasions of the Empire was the movement into Europe of the Huns. The Huns were fierce Mongol nomads from central Asia. They began invading the frontier regions of the Rhine and Danube rivers around 370 CE, destroying all in their path. The pressure from the Huns forced other groups to move into the Roman Empire as well.
The Huns Move West
The main reason for the Germanic invasions of the Empire was the movement into Europe of the Huns. The Huns were fierce Mongol nomads from central Asia. They began invading the frontier regions of the Rhine and Danube rivers around 370 CE, destroying all in their path. The pressure from the Huns forced other groups to move into the Roman Empire as well.
The following description from a fourth-century Roman historian, Ammianus Marcellinus, in his The Chronicle of Events, shows how intensely the Huns were feared and scorned:
Brain Box: How would you describe Marcelinnus' feelings about the Huns?
The people called Huns, barely mentioned in ancient records, live beyond the sea of Azof, on the border of the Frozen Ocean, and are a race savage beyond all parallel. At the very moment of birth the cheeks of their infant children are deeply marked by an iron, in order that the hair, instead of growing at the proper season on their faces, may be hindered by the scars; accordingly the Huns grow up without beards, and without any beauty. They all have closely knit and strong limbs and plump necks; they are of great size, and low legged, so that you might fancy them two-legged beasts or the stout figures which are hewn out in a rude manner with an ax on the posts at the end of bridges. They are certainly in the shape of men, however uncouth, and are so hardy that they neither require fire nor well-flavored food, but live on the roots of such herbs as they get in the fields, or on the half-raw flesh of any animal, which they merely warm rapidly by placing it between their own thighs and the backs of their horses. They never shelter themselves under roofed houses, but avoid them, as people ordinarily avoid graves, as things not fit for common use. Nor is there even to be found among them a cabin thatched with reeds; but they wander about, roaming over the mountains and the woods, and accustom themselves to bear frost and hunger and thirst from their very cradles.... There is not a person in the whole nation who cannot remain on his horse day and night. On horseback they buy and sell, they take their meat and drink, and there they recline on the narrow neck of their steed, and yield to sleep so deep as to indulge in every variety of dream. And when any deliberation is to take place on any weight matter, they all hold their common council on horseback. They are not under kingly authority, but are contented with the irregular government of their chiefs, and under their lead they force their way through all obstacles.... The nation of the Huns... surpasses all other barbarians in wildness of life.... When attacked... they fill the air with varied and discordant cries... they fight in no regular order of battle, but by being extremely swift and sudden in their movements, they disperse... spread havoc over vast plains, and... pillage the camp of their enemy almost before he has become aware of their approach.

Why was the western Roman Empire unable to stop the invasion of Germanic tribes?
Germanic Invasions
In the 4th and 5th centuries CE, many Germanic tribes took over Roman land. Some wanted better land for raising crops and farm animals. Many such as the Franks, Burgundians, and Vandals were running away from the Huns and sought refuge in Roman lands.
When the Rhine River froze during an especially cold winter in 406 CE, Vandal warriors and their families swarmed across the ice. They met little resistance and kept moving through the Roman province of Gaul. They burned buildings and took valuable things. By this time, the Western Empire was so disorganized that it was unable to field an army to stop them. Soon, the Germanic people entered every part of Roman society. Indeed, many even held high government positions.
By the early 5th century CE, the city of Rome itself was vulnerable to attack. When a tribe called the Visigoths asked Rome for protection, the Romans let them live just inside the empire's border. Later, however, the Romans treated the Visigoths badly, so the tribe fought back. in 408 CE the Visigoths, led by their king, Alaric, marched across the Alps toward Rome. It had been more than 600 years since Hannibal led the Carthaginian army through the Alps to threaten Rome. The Visigoths captured Rome in 410 CE. After first laying siege to the city, in 410 hordes of Visigoths stormed Rome and plundered it for three days.
Brain Box: Why were the Huns under Attila's command unable to take over and rule the Roman Empire?
Germanic Invasions
In the 4th and 5th centuries CE, many Germanic tribes took over Roman land. Some wanted better land for raising crops and farm animals. Many such as the Franks, Burgundians, and Vandals were running away from the Huns and sought refuge in Roman lands.
When the Rhine River froze during an especially cold winter in 406 CE, Vandal warriors and their families swarmed across the ice. They met little resistance and kept moving through the Roman province of Gaul. They burned buildings and took valuable things. By this time, the Western Empire was so disorganized that it was unable to field an army to stop them. Soon, the Germanic people entered every part of Roman society. Indeed, many even held high government positions.
By the early 5th century CE, the city of Rome itself was vulnerable to attack. When a tribe called the Visigoths asked Rome for protection, the Romans let them live just inside the empire's border. Later, however, the Romans treated the Visigoths badly, so the tribe fought back. in 408 CE the Visigoths, led by their king, Alaric, marched across the Alps toward Rome. It had been more than 600 years since Hannibal led the Carthaginian army through the Alps to threaten Rome. The Visigoths captured Rome in 410 CE. After first laying siege to the city, in 410 hordes of Visigoths stormed Rome and plundered it for three days.
Brain Box: Why were the Huns under Attila's command unable to take over and rule the Roman Empire?

Attila the Hun
Meanwhile, the Huns, who were indirectly responsible for the Germanic assault on the Empire, became a direct threat. In 444 they united for the first time under a powerful chieftain named Attila. With 100,000 soldiers, Attila terrorized both halves of the empire. In the East, his armies attacked and plundered 70 cities. They failed, however, to scale the high walls of Constantinople, the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. The Huns then swept into the West. In 452, Attila’s forces advanced against Rome. By this time, however, the Huns were weakened by famine and disease. As a result, Pope Leo I was able to negotiate their withdrawal.
After Attila’s death in 453, the Huns were no longer a threat to the empire. The Germanic invasions, however, continued. In 455, Vandals under the leadership of Gaiseric sacked Rome, leaving it in chaos. Famine struck, and Rome's population eventually dropped from about one million to 20,000.
Meanwhile, the Huns, who were indirectly responsible for the Germanic assault on the Empire, became a direct threat. In 444 they united for the first time under a powerful chieftain named Attila. With 100,000 soldiers, Attila terrorized both halves of the empire. In the East, his armies attacked and plundered 70 cities. They failed, however, to scale the high walls of Constantinople, the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire. The Huns then swept into the West. In 452, Attila’s forces advanced against Rome. By this time, however, the Huns were weakened by famine and disease. As a result, Pope Leo I was able to negotiate their withdrawal.
After Attila’s death in 453, the Huns were no longer a threat to the empire. The Germanic invasions, however, continued. In 455, Vandals under the leadership of Gaiseric sacked Rome, leaving it in chaos. Famine struck, and Rome's population eventually dropped from about one million to 20,000.
What events led to the beginning of Europe's Middle Ages ?
Rome’s Last Emperor
As Germanic tribes now fought one another for possession of the Western provinces, the Roman emperor in the West became practically powerless. Spain belonged to the Visigoths and North Africa to the Vandals. Gaul was overrun by competing tribes - Franks, Burgundians, and Visigoths. Britannia was invaded by Angles and Saxons. And, Italy fell victim to raids by the Ostrogoths.
Rome’s Last Emperor
As Germanic tribes now fought one another for possession of the Western provinces, the Roman emperor in the West became practically powerless. Spain belonged to the Visigoths and North Africa to the Vandals. Gaul was overrun by competing tribes - Franks, Burgundians, and Visigoths. Britannia was invaded by Angles and Saxons. And, Italy fell victim to raids by the Ostrogoths.
|
The last Roman emperor was a 14-year-old boy named Romulus Augustulus. In 476 he was removed from office and sent into exile by a German general named Odoacer. After that, no emperor even pretended to rule Rome and its western provinces. Roman power in the western half of the Empire had disappeared. Historians link the beginning of Europe's Middle Ages - sometimes referred to as the "Dark Ages" - to the fall of Rome in 476. The Middle Ages lasted until around 1500.
|
|
After the Fall of Rome to Odoacer, the eastern half of the Empire not only survived but flourished. It came to be called the Byzantine Empire. Byzantine emperors ruled from the city of Constantinople and saw themselves as heirs to the power of Augustus Caesar. The Byzantine Empire preserved the great heritage of Greek and Roman culture for another 1,000 years.

