Rome Unit Lessons
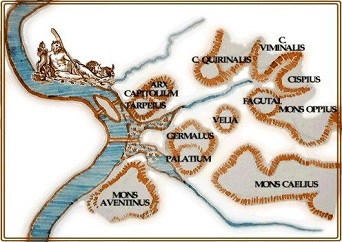
1. GEOGRAPHY
Today, Rome is often called the "Eternal City." Two thousand years ago, the world was ruled by Rome. From England to Africa and from Syria to Spain, one in every four people on earth lived and died under Roman law. During its ancient rule, Rome established a legacy of art, architecture, engineering, laws, language, and government that remains a part of our lives today. Because of that, it will be good to understand a bit about Rome's past. Rome was different from other early civilizations - bigger, more complex, some would say greater (especially if you were a proud Roman, you might say that). To understand Roman greatness, you must first understand the geographic good fortune of the Italian peninsula, good fortune that directly influenced the early settlers who called Rome home.
Today, Rome is often called the "Eternal City." Two thousand years ago, the world was ruled by Rome. From England to Africa and from Syria to Spain, one in every four people on earth lived and died under Roman law. During its ancient rule, Rome established a legacy of art, architecture, engineering, laws, language, and government that remains a part of our lives today. Because of that, it will be good to understand a bit about Rome's past. Rome was different from other early civilizations - bigger, more complex, some would say greater (especially if you were a proud Roman, you might say that). To understand Roman greatness, you must first understand the geographic good fortune of the Italian peninsula, good fortune that directly influenced the early settlers who called Rome home.

2. EARLY SETTLERS
When we think of Rome today, we either think of it’s ancient gloried past, as pictured in postcard images of the Colosseum, The Pantheon, or any number of other magnificent engineering or artistic marvels, or we think of a large European city, the capital of the nation of Italy. Of course, it is both of those things. There was a time thousands and thousands of years ago, however, when there was no Italy and Rome was just a tiny tribal village on the banks of the Tiber River. The earliest Roman settlers called themselves Latins. They settled on either side of the Tiber River in a region they called Latium. The Latins built the original settlement at Rome, a cluster of wooden huts atop one of its seven hills, the Palatine Hill. The Latins, however, were not alone in the region. They shared space on the Italian peninsula with other tribes such as the Sabines, the Umbrians, the Etruscans, as well as with Greek colonizers.
When we think of Rome today, we either think of it’s ancient gloried past, as pictured in postcard images of the Colosseum, The Pantheon, or any number of other magnificent engineering or artistic marvels, or we think of a large European city, the capital of the nation of Italy. Of course, it is both of those things. There was a time thousands and thousands of years ago, however, when there was no Italy and Rome was just a tiny tribal village on the banks of the Tiber River. The earliest Roman settlers called themselves Latins. They settled on either side of the Tiber River in a region they called Latium. The Latins built the original settlement at Rome, a cluster of wooden huts atop one of its seven hills, the Palatine Hill. The Latins, however, were not alone in the region. They shared space on the Italian peninsula with other tribes such as the Sabines, the Umbrians, the Etruscans, as well as with Greek colonizers.

3. RISE OF THE ROMAN REPUBLIC
By 600 BCE, the Etruscans were the most powerful people on the Italian peninsula. Etruscan monarchs ruled from north to south, including Rome. While the Latins before them also ruled through monarchy, the last three Roman kings were Etruscans. After ruling Rome for about 100 years, however, several factors contributed to the decline of Etruscan power and the end of monarchy in Rome. After Rome overthrew the Etruscans, they instituted a form of government known as a republic. “Republic” comes from the Latin words “res” and “publica” and literally means “thing of the people.” A republic is a type of government in which the citizens vote for their leaders. (The United States is a republic.) From its Latin roots, a republic belongs to its people, not to a king or queen. With this new form of government in place, the Romans expanded their power throughout the Italian peninsula and across the Mediterranean.
By 600 BCE, the Etruscans were the most powerful people on the Italian peninsula. Etruscan monarchs ruled from north to south, including Rome. While the Latins before them also ruled through monarchy, the last three Roman kings were Etruscans. After ruling Rome for about 100 years, however, several factors contributed to the decline of Etruscan power and the end of monarchy in Rome. After Rome overthrew the Etruscans, they instituted a form of government known as a republic. “Republic” comes from the Latin words “res” and “publica” and literally means “thing of the people.” A republic is a type of government in which the citizens vote for their leaders. (The United States is a republic.) From its Latin roots, a republic belongs to its people, not to a king or queen. With this new form of government in place, the Romans expanded their power throughout the Italian peninsula and across the Mediterranean.

4. FROM REPUBLIC TO EMPIRE
After Julius Caesar was murdered in 44 BCE, rule of Rome was shared by several competing factions. By 27 BCE, however, Caesar Augustus had defeated his rivals and consolidated his power. After a period of transition from a state of war to peace, Augustus formally announced the restoration of the republican constitution at a meeting of the Senate. While the action won him great acclaim, as did his offer to surrender his power to the Senate, everyone knew that the ancient Republic was beyond repair and that a strong government under a powerful ruler was essential to prevent a return to the chaos that had almost destroyed Rome. As a result, Caesar Augustus became Rome's first emperor. Under Augustus, Rome began a 200 year time period of peace and enormous growth. Augustus said, "I found Rome a city of bricks and left it a city of marble."
After Julius Caesar was murdered in 44 BCE, rule of Rome was shared by several competing factions. By 27 BCE, however, Caesar Augustus had defeated his rivals and consolidated his power. After a period of transition from a state of war to peace, Augustus formally announced the restoration of the republican constitution at a meeting of the Senate. While the action won him great acclaim, as did his offer to surrender his power to the Senate, everyone knew that the ancient Republic was beyond repair and that a strong government under a powerful ruler was essential to prevent a return to the chaos that had almost destroyed Rome. As a result, Caesar Augustus became Rome's first emperor. Under Augustus, Rome began a 200 year time period of peace and enormous growth. Augustus said, "I found Rome a city of bricks and left it a city of marble."

5. LIFE AS A ROMAN
The ancient Romans were one of the most advanced civilizations in history. At its peak, the Roman Empire stretched across Europe, North Africa and Asia and was home to more than 45 million people. At the Empire’s center was Rome. Rome grew into an empire, in part, because of how it treated the people it conquered. After adding a new territory to the Empire, Rome extended the rights of citizenship to the people they conquered. The Roman Empire expanded through the use of force, it’s true, but once the new people became citizens, they were Roman - no matter where they called home. Using their capital as an example, one way in which Rome controlled newly conquered populations and bound people to Rome was by building “Roman” towns throughout their Empire. In doing so, they also extended a distinctly Roman “way of life.” In this lesson, you will find out what it was like to be Roman.
The ancient Romans were one of the most advanced civilizations in history. At its peak, the Roman Empire stretched across Europe, North Africa and Asia and was home to more than 45 million people. At the Empire’s center was Rome. Rome grew into an empire, in part, because of how it treated the people it conquered. After adding a new territory to the Empire, Rome extended the rights of citizenship to the people they conquered. The Roman Empire expanded through the use of force, it’s true, but once the new people became citizens, they were Roman - no matter where they called home. Using their capital as an example, one way in which Rome controlled newly conquered populations and bound people to Rome was by building “Roman” towns throughout their Empire. In doing so, they also extended a distinctly Roman “way of life.” In this lesson, you will find out what it was like to be Roman.

6. THE EARLY CHRISTIAN CHURCH
As the Roman Empire grew in size, it became more and more difficult to govern effectively. As Roman traditions encountered the different traditions of their distant neighbors and the newly conquered, their values were challenged. Additionally, leaders governing far away from Rome became corrupt. Unrest in the provinces, combined with increasingly hostile neighbors, meant that Rome also had to spend great sums of money to support an incredibly large military. Another factor that contributed to Rome's decline, especially toward the end of Roman rule was the culture shift that happened in religion. After Rome expanded into the Middle East, they encountered belief systems such as Judaism and Christianity that were contrary to their own long-held pagan beliefs. Both Jews and Christians were persecuted by the Romans but, after the 4th century CE, Christianity, in particular, also shaped Roman rule.
As the Roman Empire grew in size, it became more and more difficult to govern effectively. As Roman traditions encountered the different traditions of their distant neighbors and the newly conquered, their values were challenged. Additionally, leaders governing far away from Rome became corrupt. Unrest in the provinces, combined with increasingly hostile neighbors, meant that Rome also had to spend great sums of money to support an incredibly large military. Another factor that contributed to Rome's decline, especially toward the end of Roman rule was the culture shift that happened in religion. After Rome expanded into the Middle East, they encountered belief systems such as Judaism and Christianity that were contrary to their own long-held pagan beliefs. Both Jews and Christians were persecuted by the Romans but, after the 4th century CE, Christianity, in particular, also shaped Roman rule.

7. AN EMPIRE DIVIDED- THE BYZANTINE EMPIRE
Known as the Byzantine Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire was its most powerful in the 500s CE. The empire stretched east to Arabia, south to Egypt, and west to Italy. Constantinople was the capital of the empire. Because the city sat between Europe and Asia, it became a crossroads for trade. As la result, Constantinople became the wealthiest part of the Roman Empire. People called Constantinople the “New Rome.” Being at the crossroads of different cultures meant that the Byzantine Empire was also something more than Roman. Different cultures blended together to form a new culture. That rich blending of cultures led the Byzantines to develop one of the most advanced civilizations in the world between 500 and 1200 CE.
Known as the Byzantine Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire was its most powerful in the 500s CE. The empire stretched east to Arabia, south to Egypt, and west to Italy. Constantinople was the capital of the empire. Because the city sat between Europe and Asia, it became a crossroads for trade. As la result, Constantinople became the wealthiest part of the Roman Empire. People called Constantinople the “New Rome.” Being at the crossroads of different cultures meant that the Byzantine Empire was also something more than Roman. Different cultures blended together to form a new culture. That rich blending of cultures led the Byzantines to develop one of the most advanced civilizations in the world between 500 and 1200 CE.

8. BARBARIANS INSIDE THE GATES
The decline of the Western Roman Empire took place over many years. Its final collapse was the result of worsening internal problems, the separation of the Western Empire from the wealthier Eastern part, and outside invasions. Since the days of Julius Caesar, Germanic peoples had gathered on the northern borders of the Empire. Some groups settled into a peaceful farming life. Eventually they adopted Roman ways, such as speaking Latin and becoming Christians. Other groups remained nomads. From 376 to 476 CE, huge numbers of Germans poured into Roman territory. As a result, Germanic tribes that included Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Franks, Angles, Saxons, Burgundians, Alemanrii, and Vandals all competed for land, recognition, and Roman favor. Gradually, they overwhelmed the structures of Roman society. Finally, they drove the last Roman emperor from the throne.
The decline of the Western Roman Empire took place over many years. Its final collapse was the result of worsening internal problems, the separation of the Western Empire from the wealthier Eastern part, and outside invasions. Since the days of Julius Caesar, Germanic peoples had gathered on the northern borders of the Empire. Some groups settled into a peaceful farming life. Eventually they adopted Roman ways, such as speaking Latin and becoming Christians. Other groups remained nomads. From 376 to 476 CE, huge numbers of Germans poured into Roman territory. As a result, Germanic tribes that included Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Franks, Angles, Saxons, Burgundians, Alemanrii, and Vandals all competed for land, recognition, and Roman favor. Gradually, they overwhelmed the structures of Roman society. Finally, they drove the last Roman emperor from the throne.

9. ROMAN REMAINS
At its heart, Roman culture reflects the characteristics of strength, loyalty, and practicality that were so highly valued in Roman society. Because Rome interacted with Greeks from the earliest periods of their history, however, the Romans also picked up Greek ideas about the "artistic ideal," a belief that everything we create is based on an ideal form. The Greeks believed that the closer our creations come to that ideal form, the more beautiful those creations are. The Romans reflected those Greek ideals in their art, architecture and writing. The result was an empire and a culture that blended Roman practicality with elements of Greek idealism and style. It is due to that unique combination of strength and beauty that Roman culture continues to inspire us today.
At its heart, Roman culture reflects the characteristics of strength, loyalty, and practicality that were so highly valued in Roman society. Because Rome interacted with Greeks from the earliest periods of their history, however, the Romans also picked up Greek ideas about the "artistic ideal," a belief that everything we create is based on an ideal form. The Greeks believed that the closer our creations come to that ideal form, the more beautiful those creations are. The Romans reflected those Greek ideals in their art, architecture and writing. The result was an empire and a culture that blended Roman practicality with elements of Greek idealism and style. It is due to that unique combination of strength and beauty that Roman culture continues to inspire us today.
10. ROME VIDEOS


