Inca Geography

Essential Themes
Geography: Why do people live and build where they do?
Review: What is geography?
Where are the Andes Mountains?
Geography: Why do people live and build where they do?
Review: What is geography?
Where are the Andes Mountains?
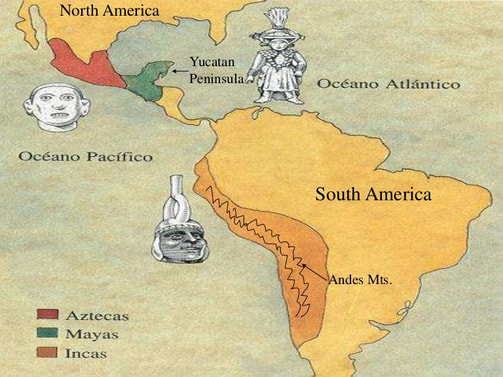
The Maya and the Aztec cultures arose in Mesoamerica, in what is now Mexico and Central America. In South America another great empire arose. That empire belonged to the Inca. South America was also home to several civilizations before the Inca built their empire. These civilizations provided a foundation for the Inca. When building their empire, the Inca borrowed from the scientific and cultural achievements - such as farming techniques and craft-making skills - of those earlier cultures.
Over 8000 years ago, people were beginning to settle the west coast of South America. By 5000 BCE they were farming the region, and by 900 BCE, complex civilizations had begun to develop in what is now Peru. Those included the Chavín (chah-VEEN) culture in the highlands, and the Nazca, Moche (MOH-chay), and Chimú (chee-MOO) cultures on the coast.
Over 8000 years ago, people were beginning to settle the west coast of South America. By 5000 BCE they were farming the region, and by 900 BCE, complex civilizations had begun to develop in what is now Peru. Those included the Chavín (chah-VEEN) culture in the highlands, and the Nazca, Moche (MOH-chay), and Chimú (chee-MOO) cultures on the coast.
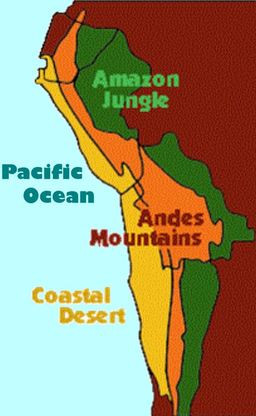
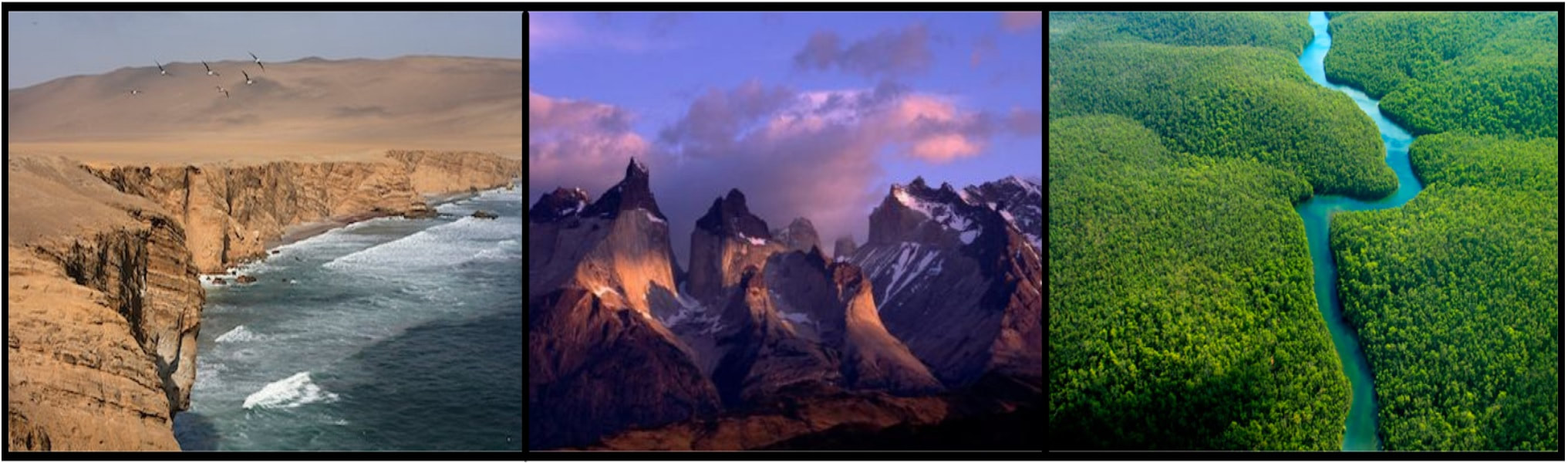
The west coast of South America can be a challenging place to build a civilization. Growth is limited by the Pacific Ocean to the west. That's left if you are looking at a map. More, the coastal region that borders the ocean is a desert. Rising from the coastal desert are the Andes Mountains. The Andes stretch north and south for 2500 miles and rise to an average elevation of about 13,000 feet. East of the mountains - that's to the right of the mountains on a map - is the Amazon jungle.
Each of the cultures that settled the area, however, learned to adapt to their environment. In doing so they made scientific advances. For example, in the steep mountains, people made terraces for farming. On the coast, they developed irrigation systems so they could farm in the desert. As a result, farming could support large populations both on the coast and in the highlands, where they built cities a full two miles above sea level.
In fact, the cities built by these early cultures were some of South America’s first. In these cities people developed crafts such as textiles, pottery, and gold jewelry. Because the cities were also religious centers, religious symbols often appeared in the crafts. The influence of these early civilizations set the stage for the Inca civilization.
Each of the cultures that settled the area, however, learned to adapt to their environment. In doing so they made scientific advances. For example, in the steep mountains, people made terraces for farming. On the coast, they developed irrigation systems so they could farm in the desert. As a result, farming could support large populations both on the coast and in the highlands, where they built cities a full two miles above sea level.
In fact, the cities built by these early cultures were some of South America’s first. In these cities people developed crafts such as textiles, pottery, and gold jewelry. Because the cities were also religious centers, religious symbols often appeared in the crafts. The influence of these early civilizations set the stage for the Inca civilization.
 Many Inca roads and bridges are still in uses today.
Many Inca roads and bridges are still in uses today.
Geography of the Inca Empire
Geography is the study of how people interact with their environment. In the 15th century CE, the Inca Indians lived high in the Andes Mountains of South America. In just 100 years, they built the largest empire in the Americas and one of the largest in the world. It was the last great empire in the Americas - an empire that was 2500 miles long, 500 miles wide, and home to over 12 million people.
The Inca were an incredible people. The Inca never invented the wheel. They never invented a system of writing. They had no use for money. Yet, high in the rugged Andes Mountains of South America, the Inca built thousands of miles of well-paved roads, kept accurate records, and enjoyed vast wealth. Everyone in the empire was well fed and no one was homeless.
Today, you are going to begin your study of a people who called themselves the "Children of the Sun." As always, you will start with geography.
Geography is the study of how people interact with their environment. In the 15th century CE, the Inca Indians lived high in the Andes Mountains of South America. In just 100 years, they built the largest empire in the Americas and one of the largest in the world. It was the last great empire in the Americas - an empire that was 2500 miles long, 500 miles wide, and home to over 12 million people.
The Inca were an incredible people. The Inca never invented the wheel. They never invented a system of writing. They had no use for money. Yet, high in the rugged Andes Mountains of South America, the Inca built thousands of miles of well-paved roads, kept accurate records, and enjoyed vast wealth. Everyone in the empire was well fed and no one was homeless.
Today, you are going to begin your study of a people who called themselves the "Children of the Sun." As always, you will start with geography.
What is a natural barrier?
Natural Barriers
The Inca civilization began in the second largest mountain range in the world, the Andes Mountains. You might guess correctly that living high in the Andes mountains was challenging. The Inca, however, were incredibly creative. Over time, the Inca not only adapted to their environment but used its benefits to thrive.
Natural barriers are features of a landscape that make crossing that land difficult. Examples of natural barriers include mountains, rivers, deserts, and deep gorges or ravines. Talk about natural barriers! The Inca empire had them all. The Inca empire covered a vast amount of space. At its height of development, the Inca empire was 2500 miles long, 500 miles wide, and home to 12 million people, connected by 25,000 miles of roads, many of which were paved. The Inca empire was located on the western side of South America. Although the empire was huge, it can be easily divided into three geographical regions: mountains, jungle, and desert.
Natural Barriers
The Inca civilization began in the second largest mountain range in the world, the Andes Mountains. You might guess correctly that living high in the Andes mountains was challenging. The Inca, however, were incredibly creative. Over time, the Inca not only adapted to their environment but used its benefits to thrive.
Natural barriers are features of a landscape that make crossing that land difficult. Examples of natural barriers include mountains, rivers, deserts, and deep gorges or ravines. Talk about natural barriers! The Inca empire had them all. The Inca empire covered a vast amount of space. At its height of development, the Inca empire was 2500 miles long, 500 miles wide, and home to 12 million people, connected by 25,000 miles of roads, many of which were paved. The Inca empire was located on the western side of South America. Although the empire was huge, it can be easily divided into three geographical regions: mountains, jungle, and desert.
What three geographic features dominated the Inca empire?
|
Andes Mountains: The Andes Mountains, home of the Inca civilization, ran north to south. The mountains dominated Inca society. The mountain peaks were worshiped as gods. The Andes created a natural barrier between the coastal desert on one side and the jungle on the other. The snow-capped mountains were full of deep gorges. The Inca built bridges across the gorges so that they could reach all parts of their empire quickly and easily. If an enemy approached, the Inca could simply burn the bridges.
|
|
 The coastal desert was home to many tribes that predate the Inca. The Nazca are known for the geoglyphs they carved into the petrified sand of the desert.
The coastal desert was home to many tribes that predate the Inca. The Nazca are known for the geoglyphs they carved into the petrified sand of the desert.
Amazon Jungle: On one side of the Andes was the Amazon jungle. The Inca must have entered the jungle occasionally, as they did know about the many valuable things that could be found in the Amazon, like wood and fruit and natural medicines. But they never established settlements there. They had no desire to live in the jungle. The Inca expanded north and south instead.
Coastal Desert: Between the mountains and the Pacific Ocean is a coastal desert 2000 miles long and 30 to 100 miles wide. The desert provided a wonderful natural barrier. Some scientists think it is the driest place in the world. It’s not completely barren, however. There are small strips of land that are made fertile by rivers and streams that run from the Andes mountain tops to the sea.
From the time of the earliest Inca settlers, the Inca used the natural barriers to their advantage. Doing so helped the Inca create a large, vibrant culture that grew into a civilization.
The Origin of the Inca
Most ancient cultures have an origin story, a story about how their civilization began. The Inca were no exception. They had many origin stories. The Inca were polytheistic, which means that they believed in a great many gods and goddesses. The Inca also loved stories, many of which had to do with their gods.
Coastal Desert: Between the mountains and the Pacific Ocean is a coastal desert 2000 miles long and 30 to 100 miles wide. The desert provided a wonderful natural barrier. Some scientists think it is the driest place in the world. It’s not completely barren, however. There are small strips of land that are made fertile by rivers and streams that run from the Andes mountain tops to the sea.
From the time of the earliest Inca settlers, the Inca used the natural barriers to their advantage. Doing so helped the Inca create a large, vibrant culture that grew into a civilization.
The Origin of the Inca
Most ancient cultures have an origin story, a story about how their civilization began. The Inca were no exception. They had many origin stories. The Inca were polytheistic, which means that they believed in a great many gods and goddesses. The Inca also loved stories, many of which had to do with their gods.
One of the legends the Incas loved to tell was about the founding of Cuzco, the capital of the Inca empire. This is the story of Manco Capac and the sun god, Inti.
Brainbox: Why did the Inca empire develop north and south, rather than east and west?
Brainbox: Why did the Inca empire develop north and south, rather than east and west?

Manco Capac: Inti, the sun god, created the first Inca from the waters of Lake Titicaca and named him Manco Capac. The sun god created a sister for Manco and named her Mama Ocllo. The sun god told Manco and Mama to go on a journey. Their job was to search high and low for a special place called Cuzco, which means "the center of the world." The sun god gave Manco Capac a golden staff. The sun god said, “You will know that you have found the center of the world when the staff is swallowed by the earth. When you find that spot you will build a city and you will name that city Cuzco. In this special city, you will teach others about the power of the sun god.”
Because no one argued with the sun god, Manco Capac and his sister immediately traveled into the harsh Andes Mountains and walked north. Things were looking pretty grim. Though they tried over and over, Manco and Mama could not find a place where they could sink the golden staff into the ground.
Faithful to the command of Inti, the sun god, Manco Capac and Mama Ocllo traveled on. After traveling for many generations and exhausted, one day they came upon the most beautiful location they had ever seen. When Manco tested the ground, his staff sank immediately out of sight, just as the sun god had foretold. Manco Capac and his sister built their city on that spot. They named their city Cuzco.
Because no one argued with the sun god, Manco Capac and his sister immediately traveled into the harsh Andes Mountains and walked north. Things were looking pretty grim. Though they tried over and over, Manco and Mama could not find a place where they could sink the golden staff into the ground.
Faithful to the command of Inti, the sun god, Manco Capac and Mama Ocllo traveled on. After traveling for many generations and exhausted, one day they came upon the most beautiful location they had ever seen. When Manco tested the ground, his staff sank immediately out of sight, just as the sun god had foretold. Manco Capac and his sister built their city on that spot. They named their city Cuzco.
|
|
There were other tribes in the area, but Manco Capac soon took over leadership of all the tribes. Manco Capac became the first ruler of the Inca. That’s how Cuzco became not just the center of the world but also the capital of the Inca empire.
Manco Capac went on to have 400 children. When he died at a very old age, the Inca built the Temple of the Sun on the spot where he died. |
Brainbox: What does Manco Capac's golden staff represent?


