Greece Geography

Essential Themes
1. Geography: Why do people move and live where they do?
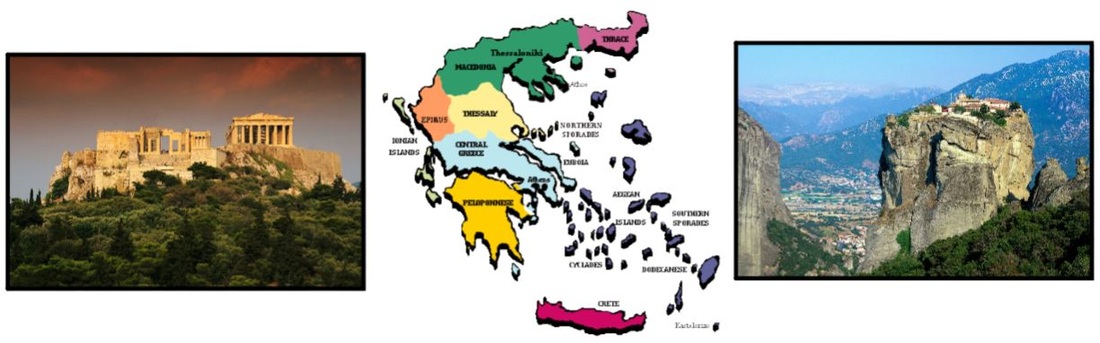
As you know, geography is the study of how humans interact with their environment. Just as geography played a major role in how the civilizations of Mesopotamia, Egypt, China, and India developed, the geography of Greece determined how Greek culture grew and spread throughout the ancient world. The geography of Greece, however, is different from the geography of the other civilizations that you have studied this year. Greece is small compared to the other civilizations you've studied, yet it rose to unparalleled greatness and its influence is still felt today. Because of its rich legacy of artistic, political, and philosophical achievements, many consider Greece to be the true birthplace of Western civilization.
To better understand how Greece rose to greatness, we must begin by taking a look at its geography. To do so, let's begin with the story of "Pathos the Farmer." In your first activity, you'll work with partners to create a map of ancient Greece. Therefore, while you read the story, underline or highlight the parts of the text that you think will be useful in creating your map.
1. Geography: Why do people move and live where they do?
As you know, geography is the study of how humans interact with their environment. Just as geography played a major role in how the civilizations of Mesopotamia, Egypt, China, and India developed, the geography of Greece determined how Greek culture grew and spread throughout the ancient world. The geography of Greece, however, is different from the geography of the other civilizations that you have studied this year. Greece is small compared to the other civilizations you've studied, yet it rose to unparalleled greatness and its influence is still felt today. Because of its rich legacy of artistic, political, and philosophical achievements, many consider Greece to be the true birthplace of Western civilization.
To better understand how Greece rose to greatness, we must begin by taking a look at its geography. To do so, let's begin with the story of "Pathos the Farmer." In your first activity, you'll work with partners to create a map of ancient Greece. Therefore, while you read the story, underline or highlight the parts of the text that you think will be useful in creating your map.
Review: What is a city-state?
 Blue seas, narrow beaches, and rugged terrain characterize the coastline of Greece.
Blue seas, narrow beaches, and rugged terrain characterize the coastline of Greece.
Readers Theater: Pathos the Farmer
Narrator 1: The land of ancient Greece lies along the northern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. To the west is present day Italy and Europe. To the east is Turkey, known to the Greeks as Anatolia, and the nations of the Middle-East. The northern coast of Africa, including Egypt, sits to the south. Because of this prominent and strategic geographical position, Greece was able to establish itself as a major power of the ancient world.
Narrator 2: Many geographical factors shaped the culture and history of the ancient civilizations. Let's travel back in time to visit with Pathos, a farmer, and his family and friends. They will tell you of the wonders of this unique land and give you a tour of a typical farm in Ancient Greece.
Narrator 1: The land of ancient Greece lies along the northern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. To the west is present day Italy and Europe. To the east is Turkey, known to the Greeks as Anatolia, and the nations of the Middle-East. The northern coast of Africa, including Egypt, sits to the south. Because of this prominent and strategic geographical position, Greece was able to establish itself as a major power of the ancient world.
Narrator 2: Many geographical factors shaped the culture and history of the ancient civilizations. Let's travel back in time to visit with Pathos, a farmer, and his family and friends. They will tell you of the wonders of this unique land and give you a tour of a typical farm in Ancient Greece.
What is the name of the first Greek civilization, and where did it develop?
 Above, a typical Greek olive farm nestled in a mountain valley.
Above, a typical Greek olive farm nestled in a mountain valley.
Pathos: Welcome my friends. Greece is not an easy place to live. The soil is not very good for growing things, there are a lot of mountains that make it hard to walk from one place to another, and there is never enough fresh water. Because of this, people did not settle in Greece as early as they did in Egypt, India, China, or the Fertile Crescent. On the other hand, what Greece does have a lot of is coastline. We live bounded by water. Our natural barriers include the Aegean, Ionian, and Mediterranean Seas.
Many people live on the mainland, or on the Peloponnesus Peninsula, and many others have settled on the thousands of islands off-shore. The very first Greek civilization, the Minoan, was established on the large southern island of Crete. As with most Greek settlements, its development was greatly influenced by the sea and the land.
80% of Greek land is covered by mountains, so farming is limited to the foothills near the coast and to valleys between the mountains. The mountains also make travel over land difficult. Therefore, most of the population live within one day's journey of the coast. Of course, most Greek cities also exist within that narrow coastal band. As a result of their geography, the Greeks have always depended on the sea for fishing, trade, and to travel between city-states.
Many people live on the mainland, or on the Peloponnesus Peninsula, and many others have settled on the thousands of islands off-shore. The very first Greek civilization, the Minoan, was established on the large southern island of Crete. As with most Greek settlements, its development was greatly influenced by the sea and the land.
80% of Greek land is covered by mountains, so farming is limited to the foothills near the coast and to valleys between the mountains. The mountains also make travel over land difficult. Therefore, most of the population live within one day's journey of the coast. Of course, most Greek cities also exist within that narrow coastal band. As a result of their geography, the Greeks have always depended on the sea for fishing, trade, and to travel between city-states.
What is a peninsula?

Dela: Other groups eventually settled on the Peloponnesus Peninsula. A peninsula is a body of land surrounded on three sides by water. Greece has many small and large peninsulas. The Peloponnesus Peninsula, shown to the right, is connected to the mainland by a narrow isthmus. Still more groups settle on the many islands scattered in the Aegean Sea. Since most of Greece is very mountainous, however, the mountains divide the mainland and the islands into small, isolated regions. These natural barriers make communication between the different settlements very difficult. As a result, we have formed many close-knit communities independent of one another. We consider ourselves citizens of a local community rather than of a nation.
Narrator 3: Although they were really more like small towns, we now call these groups city-states. The rivalries between these many city-states became key issues in Greek history. What united these people and made them all Greek? It was their religious belief system, their cultural similarities, and the stories they shared, all things that were shaped by Greece's unique terrain.
Narrator 3: Although they were really more like small towns, we now call these groups city-states. The rivalries between these many city-states became key issues in Greek history. What united these people and made them all Greek? It was their religious belief system, their cultural similarities, and the stories they shared, all things that were shaped by Greece's unique terrain.
What are three ways in which the sea influenced early Greek life?
 Minoan art shows how vital the seas were to early Greek life..
Minoan art shows how vital the seas were to early Greek life..
Acropis: In addition to the mountains and the islands, the sea has directly influenced the development of Greek civilization and culture. The sea has become our vital link between communities on the mainland and the islands. More and more people now travel by sea, allowing us to share ideas and trade. Mastering travel on the seas has allowed us to build a powerful navy and gain a common identity.
Narrator 4: Greek art has always been inspired by the sea, the mountains, and the islands. They became the source for many tales of adventure, as well as many fears. Because people were cut off from other communities, the wild tales brought by travelers claiming to have visited lands with unusual creatures and powers were believed. Eventually, these tales became a part of the Greek culture itself. Today, we enjoy those stories as Greek mythology.
Zetu: As my friends have mentioned, Greece is a land of high mountains. These mountains were once covered by trees, but as our population grew we irresponsibly cleared them. As we cleared the trees, the good soil washed away. This means that we have a limited amount of space suitable for growing crops. This is unfortunate because our hot and sunny climate would allow crops to grow year-round.
Even though our dry land cannot support large herds of animals, we do use oxen, mules, and donkeys to pull carts. We keep pigs and poultry to provide luxury foods at dinner parties. Our most common animal is the goat, which lives happily in our dry climate. They provide milk, meat, and skins. The very rich own land with lush plant life, so they are able to also raise horses.
Narrator 4: Greek art has always been inspired by the sea, the mountains, and the islands. They became the source for many tales of adventure, as well as many fears. Because people were cut off from other communities, the wild tales brought by travelers claiming to have visited lands with unusual creatures and powers were believed. Eventually, these tales became a part of the Greek culture itself. Today, we enjoy those stories as Greek mythology.
Zetu: As my friends have mentioned, Greece is a land of high mountains. These mountains were once covered by trees, but as our population grew we irresponsibly cleared them. As we cleared the trees, the good soil washed away. This means that we have a limited amount of space suitable for growing crops. This is unfortunate because our hot and sunny climate would allow crops to grow year-round.
Even though our dry land cannot support large herds of animals, we do use oxen, mules, and donkeys to pull carts. We keep pigs and poultry to provide luxury foods at dinner parties. Our most common animal is the goat, which lives happily in our dry climate. They provide milk, meat, and skins. The very rich own land with lush plant life, so they are able to also raise horses.
 A typical Greek farm.
A typical Greek farm.
Dorian: Come now and visit our family farmlands. We grow our crops in the hill country that lies between the coastal plains and the mountains. Many farmers, like my father, build terraces on the slopes to increase their farmland. Here we grow grapes, olives, pears, apples, and pomegranates. Other important crops include peas and beans. Since grain is in short supply, we trade our crops with other countries for much needed grains like wheat and barley. Wheat and barley are made into bread, porridge, and beer. My parents will accompany you to the next ridge and you can watch Plutos as he plows the fields with our other workers.
Plutos: My plow is made from the curved branch of a tree that is dragged through the soil by an ox. Behind me walks the sower, who scatters seeds in my footsteps. At harvest time we will cut the crops with a curved blade called a sickle. If you look beyond my field you can see Pathos' olive grove. Olive trees flourish in this dry, rocky soil. It is now harvest time for the olives. One man sits in the tree and shakes the branches while others below gather the fallen fruits in their baskets.
Plutos: My plow is made from the curved branch of a tree that is dragged through the soil by an ox. Behind me walks the sower, who scatters seeds in my footsteps. At harvest time we will cut the crops with a curved blade called a sickle. If you look beyond my field you can see Pathos' olive grove. Olive trees flourish in this dry, rocky soil. It is now harvest time for the olives. One man sits in the tree and shakes the branches while others below gather the fallen fruits in their baskets.
What crops are able to thrive in Greece?
|
Pathos: Olives and grapes are our most prevalent and useful crops.The fruit of the olive can be eaten or crushed to make cooking oil and for eating on bread. We also use olive oil with scented herbs to clean and moisturize our skin instead of soap. Olive oil is essential for use in our clay lamps, which provide the main form of light in our homes. We believe that the goddess, Athena, gave the gift of the olive tree to the Greeks by striking her spear into the rock of the Acropolis. From this spot grew the first olive tree.
Dela: Grapes also provide a food source of fruit. They are crushed to make juice or wine. Grape and olive products are easy to grow here and are useful for trade with other countries, as is honey. Honey is the only sweetener used throughout the world we know. Beekeeping is widespread throughout Greece. Narrator 5: As you have learned, the unique geography of Greece was influential in shaping its economy, culture, and history. The Greeks' power on the sea allowed them to make contact with other people and countries. They evolved into a civilization that, while influenced by others, remained distinctive in their beliefs and way of life. Brain Box: How would you describe the geography of Greece?
|