Greece The Age of Heroes

Essential Themes
5. Conflict and Cooperation: How has warfare shaped human history?
7. Culture: How do we know what we know about human history?
Welcome to the Age of Heroes
As the Minoan Civilization weakened, a group of people called the Mycenaeans were growing ever stronger on the Peloponnesus Peninsula area of the Greek mainland. A close reading of "Theseus and the Minotaur," tells the reader that the Mycenaeans were once subordinate to the power of the Minoans. While that is true, it is also true that the Mycenaeans learned quite a lot from the Minoans during that time of subordination. They began to build their homes in the Minoan style and much of their art mimicked Minoan art. Just as the Minoans had done, the Mycenaeans also built a strong fleet of ships. With a strong navy, the Mycenaeans were able to capture trade routes and establish colonies on islands in the Aegean and along the coast of Asia Minor, modern-day Turkey.
5. Conflict and Cooperation: How has warfare shaped human history?
7. Culture: How do we know what we know about human history?
Welcome to the Age of Heroes
As the Minoan Civilization weakened, a group of people called the Mycenaeans were growing ever stronger on the Peloponnesus Peninsula area of the Greek mainland. A close reading of "Theseus and the Minotaur," tells the reader that the Mycenaeans were once subordinate to the power of the Minoans. While that is true, it is also true that the Mycenaeans learned quite a lot from the Minoans during that time of subordination. They began to build their homes in the Minoan style and much of their art mimicked Minoan art. Just as the Minoans had done, the Mycenaeans also built a strong fleet of ships. With a strong navy, the Mycenaeans were able to capture trade routes and establish colonies on islands in the Aegean and along the coast of Asia Minor, modern-day Turkey.
Brain Box: What is a Hero?
The Mycenaeans believed themselves to be great warriors. They fought everyone with whom they came in contact, and many historians believe that around 1450 BCE they conquered Crete and put an end to the Minoan civilization. It was around that time that the Mycenaeans became the dominant power in the Aegean Sea region.
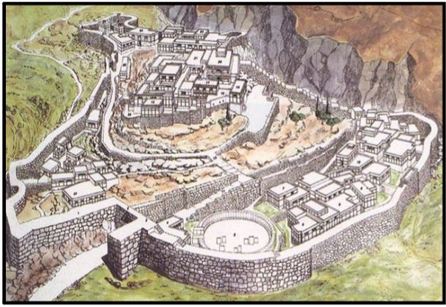
These people were named after Mycenae, the city from which they ruled. To the right is an artist's rendering of what the walled city of Mycenae may have looked like. Below is the imposing Lion's Gate that announced the power of the Mycenaeans to all who visited their city.
The Mycenaeans believed themselves to be great warriors. They fought everyone with whom they came in contact, and many historians believe that around 1450 BCE they conquered Crete and put an end to the Minoan civilization. It was around that time that the Mycenaeans became the dominant power in the Aegean Sea region.
These people were named after Mycenae, the city from which they ruled. To the right is an artist's rendering of what the walled city of Mycenae may have looked like. Below is the imposing Lion's Gate that announced the power of the Mycenaeans to all who visited their city.

Unlike the Minoans, who had ample farmlands and fishing, the hilly region in which the Mycenaeans lived lacked natural resources. As a result, the need to acquire goods from other lands led them to a life of invasion and conquest. It's possible that their warlike nature caused fighting among their colonies and that the constant infighting eventually resulted in the collapse of their own civilization. By 1200 BCE, the Mycenaean culture was weak and had become a target for invaders from the north, the Dorians.
Historians and archaeologists have found written records left by the Mycenaeans that tell how they tried to save their women and children by moving them from one town to another, and how they stockpiled war material in preparation for the next battle with the Dorians. The Mycenaeans were great warriors, but the Dorians had iron weapons. The Mycenaeans really didn’t stand a chance against such superior equipment.
All of the Mycenaean cities fell to the Dorians except for Athens. Historians believe that a secret underground supply of water in the Acropolis was the salvation of Athens. As a consequence of being able to withstand a siege by the Dorians, Athenian culture was preserved during Dorian rule and it's that culture that later set the stage for the Classical, or Golden Age of Greece.
Historians and archaeologists have found written records left by the Mycenaeans that tell how they tried to save their women and children by moving them from one town to another, and how they stockpiled war material in preparation for the next battle with the Dorians. The Mycenaeans were great warriors, but the Dorians had iron weapons. The Mycenaeans really didn’t stand a chance against such superior equipment.
All of the Mycenaean cities fell to the Dorians except for Athens. Historians believe that a secret underground supply of water in the Acropolis was the salvation of Athens. As a consequence of being able to withstand a siege by the Dorians, Athenian culture was preserved during Dorian rule and it's that culture that later set the stage for the Classical, or Golden Age of Greece.
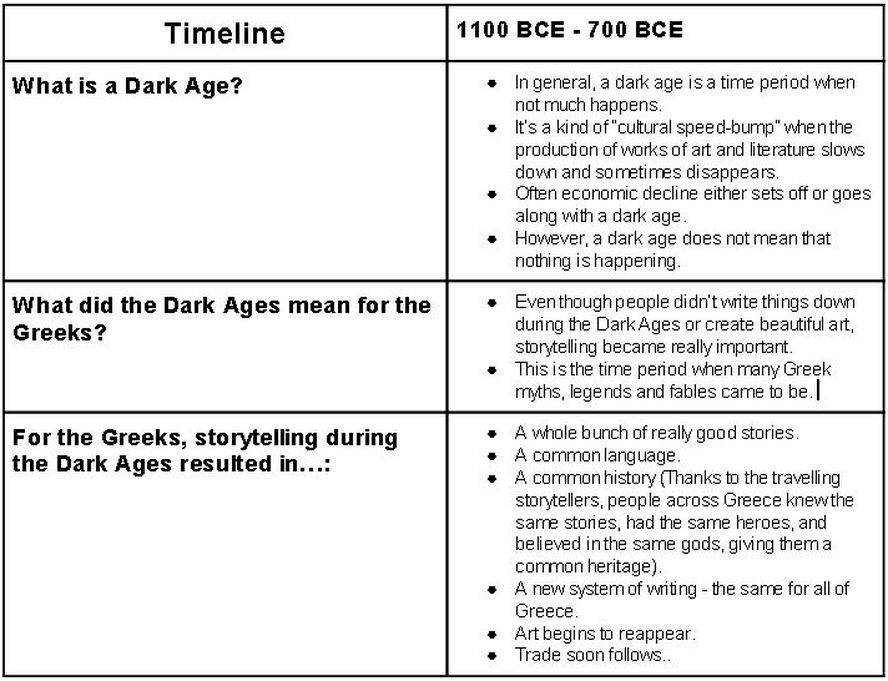
What is a dark age?
The Greek Dark Ages
The Dorians were uncivilized people who possessed none of the skills or craftsmanship of the Minoans or the Mycenaeans. When the Dorians completed their conquest, the impressive towns of the Mycenaeans were replaced with small, poor villages. Fine silver and gold decorated vases were replaced with simple pots.The Dorians were farmers rather than traders and, as you know, the Greek mainland had few opportunities for robust farming. As a result, trade during Dorian rule came to a standstill. The Dorians had no written language and around 1200 BCE all written records seem to simply stop.
The Dorians were uncivilized people who possessed none of the skills or craftsmanship of the Minoans or the Mycenaeans. When the Dorians completed their conquest, the impressive towns of the Mycenaeans were replaced with small, poor villages. Fine silver and gold decorated vases were replaced with simple pots.The Dorians were farmers rather than traders and, as you know, the Greek mainland had few opportunities for robust farming. As a result, trade during Dorian rule came to a standstill. The Dorians had no written language and around 1200 BCE all written records seem to simply stop.

Tracing the course of pottery-making during the time period is one way to view the affect the dark ages had on Greek culture. At the very left is a late Mycenaean pot followed by a drinking cup from early Dorian rule. It seems that a lot of the dark age pottery was made at home by people who apparently didn't know much about the craft. Much of pottery from this time appears lumpy, lopsided, and is presented with little decoration. The next pot was made during the middle-dark ages, while the last pot was created late in the dark ages.
With the arrival of the Dorians, Greece entered a period of decline and fell into a Dark Age. A Dark Age is a period of time in history when artistic and economic activity slow down and sometimes disappear. The Dark Age of ancient Greece lasted until around 800 BCE, about 400 years. While Greece was in a Dark Age, however, it was not wasted time. During the dark ages, a great deal happened.
What led to the end of the Greek dark ages?

By the end of the Dark Ages the Greeks had begun to look to their past, their history as it were, as a source of inspiration. Tales of Greek greatness emerged from their "age of heroes," the age when the Mycenaeans ruled the region. Those tales were spread throughout Greece by wandering storytellers who traveled from town to town bringing news and entertaining the people with fabulous tales of heroes, gods, and mythical monsters.
The most famous of those storytellers, Homer, is pictured at right. Homer is credited with writing the Iliad and the Odyssey, stories about the war Greece fought against the Trojans and Odysseus' long journey home after the conflict. Because of the storytellers, an advanced culture emerged. It was out of that culture that the Golden Age of Greece blossomed, an era that all generations look to as one of the great time periods in all of world history. It is to those wandering storytellers, therefore, that we all owe a great debt of gratitude. It might even be said that it was the storytellers and the tales they told that led to the end of the Dark Ages in ancient Greece.
The most famous of those storytellers, Homer, is pictured at right. Homer is credited with writing the Iliad and the Odyssey, stories about the war Greece fought against the Trojans and Odysseus' long journey home after the conflict. Because of the storytellers, an advanced culture emerged. It was out of that culture that the Golden Age of Greece blossomed, an era that all generations look to as one of the great time periods in all of world history. It is to those wandering storytellers, therefore, that we all owe a great debt of gratitude. It might even be said that it was the storytellers and the tales they told that led to the end of the Dark Ages in ancient Greece.
What are three things that came out of the dark ages of ancient Greece?

Several important things came out of the ancient story telling tradition that began during the dark ages of ancient Greece.
Language: The Greeks developed a common language. Before the Dorians, people in various sections of Greece spoke different languages. By the end of the dark ages, nearly everybody spoke Greek. That happened because of the traveling storytellers. The Greeks loved stories, especially epic stories about heroes and mythical beings. To understand the stories, they had to speak the language of the storytellers. For the storytellers to be popular, they had to speak the language of the people. In time, everyone spoke the same language – Greek.
The Greek Alphabet: The Greeks developed a common system of writing. By the end of the dark ages, a new system of writing had been invented. The same system of writing was used all over Greece.
Language: The Greeks developed a common language. Before the Dorians, people in various sections of Greece spoke different languages. By the end of the dark ages, nearly everybody spoke Greek. That happened because of the traveling storytellers. The Greeks loved stories, especially epic stories about heroes and mythical beings. To understand the stories, they had to speak the language of the storytellers. For the storytellers to be popular, they had to speak the language of the people. In time, everyone spoke the same language – Greek.
The Greek Alphabet: The Greeks developed a common system of writing. By the end of the dark ages, a new system of writing had been invented. The same system of writing was used all over Greece.

The Polis: They developed a new political system, the city-state. Before the dark ages, kings ruled people. The polis or city-state replaced the king-ruled system in many parts of Greece. In the polis, all citizens had rights and duties.
Mythical Beings: They worshiped the same gods. Thanks to the storytellers, all the ancient Greeks knew the many stories of the gods and goddesses. They heard them over and over, until they knew and believed every word.
Heroes: History is the stories we tell. Thanks to the storytellers during the Greek Dark Ages, the ancient Greeks all knew the stories of the many heroes from their past, heroes from Mycenaean times. They knew the story of how Theseus liberated the Greeks from Minoan domination. They knew about the legendary leadership of King Agamemnon. The story of the siege of Troy became common knowledge, a past shared by all. They memorized the stories of Achilles and the adventure tales of Odysseus. Those names were the names of heroes. They were their heroes, Greek heroes. It gave them great pride and, more importantly, it gave them a common history.
The End of the Dark Age: About 700 B.C.E., the Greeks left their dark age behind, and began to grow into the powerful city-states of ancient Greece.
Mythical Beings: They worshiped the same gods. Thanks to the storytellers, all the ancient Greeks knew the many stories of the gods and goddesses. They heard them over and over, until they knew and believed every word.
Heroes: History is the stories we tell. Thanks to the storytellers during the Greek Dark Ages, the ancient Greeks all knew the stories of the many heroes from their past, heroes from Mycenaean times. They knew the story of how Theseus liberated the Greeks from Minoan domination. They knew about the legendary leadership of King Agamemnon. The story of the siege of Troy became common knowledge, a past shared by all. They memorized the stories of Achilles and the adventure tales of Odysseus. Those names were the names of heroes. They were their heroes, Greek heroes. It gave them great pride and, more importantly, it gave them a common history.
The End of the Dark Age: About 700 B.C.E., the Greeks left their dark age behind, and began to grow into the powerful city-states of ancient Greece.